2020-03-13
React-Native 실행 환경설정
맥(Mac)에 React Native 개발 환경 구축하기
이 블로그의 설정 방법을 따라가면서 React-Native 실행환경을 설정했다.
성공!
JavaScript 문법
삼항연산자
condition ? true : false
- 한 줄이 너무 길 때
let text = array.length === 0 ? `배열이 비어있다.` : `배열이 비어있지 않다`;
let text = array.length === 0 ? `배열이 비어있다.` : `배열이 비어있지 않다`;
Truthy and Falsy
undefined 와 null 은 모두 false 로 간주됨.
Falsy 한 값
undefinednull0NaNfalse
이 외에는 모두 true 로 간주됨
! , !! 를 활용해 Falsy 한 값과 Truthy 한 값을 한번에 처리할 수 있음
단축 평가 논리 계산법
A && B 연산자를 사용할 때 A가 Truthy 한 값이라면, B가 결과값이 되고, Falsy 한 값이라면, A가 출력된다.
console.log(true && 'hello'); // hello
console.log(false && 'hello'); // false
console.log('hello' && 'bye'); // bye
console.log(null && 'hello'); // null
console.log(undefined && 'hello'); // undefined
console.log('' && 'hello'); // ''
console.log(0 && 'hello'); // 0
console.log(1 && 'hello'); // hello
console.log(1 && 1); // 1
console.log(true && 'hello'); // hello
console.log(false && 'hello'); // false
console.log('hello' && 'bye'); // bye
console.log(null && 'hello'); // null
console.log(undefined && 'hello'); // undefined
console.log('' && 'hello'); // ''
console.log(0 && 'hello'); // 0
console.log(1 && 'hello'); // hello
console.log(1 && 1); // 1
A || B 연산자는 만약 A가 Truthy 한 값이라면, A가 결과값이 되고, Falsy 한값이라면 B가 출력된다.
console.log(true || 'hello'); // true
console.log(false || 'hello'); // hello
console.log('hello' || 'bye'); // hello
console.log(null || 'hello'); // hello
console.log(undefined || 'hello'); // undefined
console.log('' || 'hello'); // hello
console.log(0 || 'hello'); // hello
console.log(1 || 'hello'); // 1
console.log(1 || 1); // 1
console.log(true || 'hello'); // true
console.log(false || 'hello'); // hello
console.log('hello' || 'bye'); // hello
console.log(null || 'hello'); // hello
console.log(undefined || 'hello'); // undefined
console.log('' || 'hello'); // hello
console.log(0 || 'hello'); // hello
console.log(1 || 'hello'); // 1
console.log(1 || 1); // 1
함수의 기본 파라미터
파라미터에서 = 기호를 사용해 기본값을 설정할 수 있다.
function calculateCircleArea(r = 1) {
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
const area = calculateCircleArea();
console.log(area); // 3.141592653589793
function calculateCircleArea(r = 1) {
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
const area = calculateCircleArea();
console.log(area); // 3.141592653589793
조건문 더 스마트하게 쓰기
- 특정 값이 여러 값 중 하나인지 확인해야 할 때
function isAnimal(text) {
return (
text === '고양이' || text === '개' || text === '거북이' || text === '너구리'
);
}
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false
function isAnimal(text) {
return (
text === '고양이' || text === '개' || text === '거북이' || text === '너구리'
);
}
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false
배열의 includes 함수를 사용
function isAnimal(name) {
const animals = ['고양이', '개', '거북이', '너구리'];
return animals.includes(name);
}
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false
function isAnimal(name) {
const animals = ['고양이', '개', '거북이', '너구리'];
return animals.includes(name);
}
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false
화살표 함수 사용
const isAnimal = (name) => ['고양이', '개', '거북이', '너구리'].includes(name);
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false
const isAnimal = (name) => ['고양이', '개', '거북이', '너구리'].includes(name);
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false
- 값에 따라 다른 결과물을 반환해야 할 때
function getSound(animal) {
if (animal === '개') return '멍멍!';
if (animal === '고양이') return '야옹~';
if (animal === '참새') return '짹짹';
if (animal === '비둘기') return '구구 구 구';
return '...?';
}
function getSound(animal) {
if (animal === '개') return '멍멍!';
if (animal === '고양이') return '야옹~';
if (animal === '참새') return '짹짹';
if (animal === '비둘기') return '구구 구 구';
return '...?';
}
switch 사용
function getSound(animal) {
switch (animal) {
case '개':
return '멍멍!';
case '고양이':
return '야옹~';
case '참새':
return '짹짹';
case '비둘기':
return '구구 구 구';
default:
return '...?';
}
}
console.log(getSound('개')); // 멍멍!
console.log(getSound('비둘기')); // 구구 구 구
function getSound(animal) {
switch (animal) {
case '개':
return '멍멍!';
case '고양이':
return '야옹~';
case '참새':
return '짹짹';
case '비둘기':
return '구구 구 구';
default:
return '...?';
}
}
console.log(getSound('개')); // 멍멍!
console.log(getSound('비둘기')); // 구구 구 구
객체 활용
function getSound(animal) {
const sounds = {
개: '멍멍!',
고양이: '야옹~',
참새: '짹짹',
비둘기: '구구 구 구',
};
return sounds[animal] || '...?';
}
console.log(getSound('개')); // 멍멍!
console.log(getSound('비둘기')); // 구구 구 구
function getSound(animal) {
const sounds = {
개: '멍멍!',
고양이: '야옹~',
참새: '짹짹',
비둘기: '구구 구 구',
};
return sounds[animal] || '...?';
}
console.log(getSound('개')); // 멍멍!
console.log(getSound('비둘기')); // 구구 구 구
- 값에 따라 다른 코드 구문을 실행할 때
function makeSound(animal) {
const tasks = {
개() {
console.log('멍멍');
},
고양이() {
console.log('고양이');
},
비둘기() {
console.log('구구 구 구');
},
};
if (!tasks[animal]) {
console.log('...?');
return;
}
tasks[animal]();
}
makeSound('개');
makeSound('비둘기');
function makeSound(animal) {
const tasks = {
개() {
console.log('멍멍');
},
고양이() {
console.log('고양이');
},
비둘기() {
console.log('구구 구 구');
},
};
if (!tasks[animal]) {
console.log('...?');
return;
}
tasks[animal]();
}
makeSound('개');
makeSound('비둘기');
비구조화 할당 (구조분해) 문법
비구조화 할당
const object = {a: 1, b: 2};
const {a, b} = object;
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(b); // 2
const object = {a: 1, b: 2};
const {a, b} = object;
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(b); // 2
- 함수의 파라미터
const object = {a: 1, b: 2};
function print({a, b}) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
print(object);
const object = {a: 1, b: 2};
function print({a, b}) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
print(object);
비구조화 할당시 기본값 설정
const object = {a: 1};
const {a, b = 2} = object;
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(b); // 2
const object = {a: 1};
const {a, b = 2} = object;
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(b); // 2
- 함수의 파라미터
const object = {a: 1};
function print({a, b = 2}) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
print(object);
// 1
// 2
const object = {a: 1};
function print({a, b = 2}) {
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
print(object);
// 1
// 2
비구조화 할당시 이름 바꾸기
const animal = {
name: '멍멍이',
type: '개',
};
const nickname = animal.name;
console.log(nickname); // 멍멍이
const animal = {
name: '멍멍이',
type: '개',
};
const nickname = animal.name;
console.log(nickname); // 멍멍이
animal.name 값을 nickname 값에 담고 있다. 이를 비구조화 할당을 사용한다면,
const animal = {
name: '멍멍이',
type: '개',
};
const {name: nickname} = animal;
console.log(nickname);
const animal = {
name: '멍멍이',
type: '개',
};
const {name: nickname} = animal;
console.log(nickname);
: 문자를 사용해서 이름을 바꿔줄 수 있다.
배열 비구조화 할당
const array = [1, 2];
const [one, two] = array;
console.log(one);
console.log(two);
const array = [1, 2];
const [one, two] = array;
console.log(one);
console.log(two);
배열 안에 있는 원소를 다른 이름을 새로 선언해주고 싶을 때 사용하면 유용. 객체 비구조화 할당과 마찬가지로 기본값 지정이 가능.
const array = [1];
const [one, two = 2] = array;
console.log(one);
console.log(two);
const array = [1];
const [one, two = 2] = array;
console.log(one);
console.log(two);
깊은 값 비구조화 할당
const deepObject = {
state: {
information: {
name: 'younho9',
languages: ['korean', 'english', 'chinese'],
},
},
value: 5,
};
const deepObject = {
state: {
information: {
name: 'younho9',
languages: ['korean', 'english', 'chinese'],
},
},
value: 5,
};
여기서 name , languages , value 값을 밖으로 꺼내고 싶을 때
const deepObject = {
state: {
information: {
name: 'younho9',
languages: ['korean', 'english', 'chinese'],
},
},
value: 5,
};
const {name, languages} = deepObject.state.information;
const {value} = deepObject;
const extracted = {
name,
languages,
value,
};
console.log(extracted); // {name: "younho9", languages: Array[3], value: 5}
const deepObject = {
state: {
information: {
name: 'younho9',
languages: ['korean', 'english', 'chinese'],
},
},
value: 5,
};
const {name, languages} = deepObject.state.information;
const {value} = deepObject;
const extracted = {
name,
languages,
value,
};
console.log(extracted); // {name: "younho9", languages: Array[3], value: 5}
아래의 코드는 다음과 같다
const extracted = {
name: name,
languages: languages,
value: value,
};
const extracted = {
name: name,
languages: languages,
value: value,
};
다른 방법은
const deepObject = {
state: {
information: {
name: 'younho9',
languages: ['korean', 'english', 'chinese'],
},
},
value: 5,
};
const {
state: {
information: {name, languages},
},
value,
} = deepObject;
const extracted = {
name,
languages,
value,
};
console.log(extracted);
const deepObject = {
state: {
information: {
name: 'younho9',
languages: ['korean', 'english', 'chinese'],
},
},
value: 5,
};
const {
state: {
information: {name, languages},
},
value,
} = deepObject;
const extracted = {
name,
languages,
value,
};
console.log(extracted);
이렇게 하는 방법도 있다.
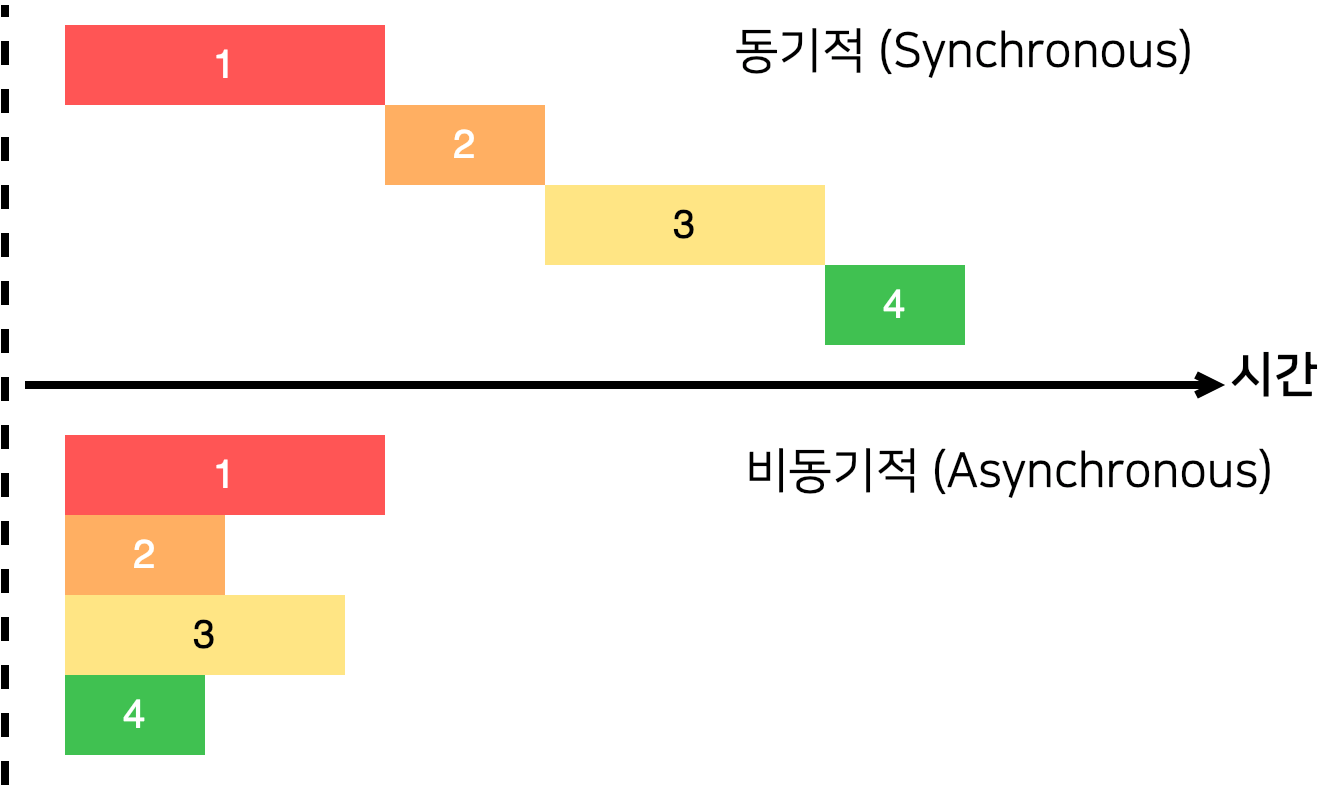
자바스크립트에서 비동기 처리 다루기
function work() {
const start = Date.now();
for (let i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {}
const end = Date.now();
console.log(end - start + 'ms');
}
work();
console.log('다음 작업');
function work() {
const start = Date.now();
for (let i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {}
const end = Date.now();
console.log(end - start + 'ms');
}
work();
console.log('다음 작업');
work() 를 수행하는 동안 다음 작업이 진행되지 않는다.
이를 비동기적으로 처리하게 만들고 싶다. → setTImeout() 함수 사용
function work() {
setTimeout(() => {
const start = Date.now();
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {}
const end = Date.now();
console.log(end - start + 'ms');
}, 0);
}
console.log('작업 시작!');
work();
console.log('다음 작업');
function work() {
setTimeout(() => {
const start = Date.now();
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {}
const end = Date.now();
console.log(end - start + 'ms');
}, 0);
}
console.log('작업 시작!');
work();
console.log('다음 작업');
먼저 work() 이후의 작업을 실행하고 work() 는 백그라운드에서 실행한다.
만약 비동기적으로 처리하면서 work() 함수가 끝난 이후에 어떤 작업을 처리하게 만들어주고 싶다면, 콜백 함수를 사용할 수 있다.
function work(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const start = Date.now();
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {}
const end = Date.now();
console.log(end - start + 'ms');
callback();
}, 0);
}
console.log('작업 시작!');
work(() => {
console.log('작업이 끝났어요!');
});
console.log('다음 작업');
function work(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const start = Date.now();
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {}
const end = Date.now();
console.log(end - start + 'ms');
callback();
}, 0);
}
console.log('작업 시작!');
work(() => {
console.log('작업이 끝났어요!');
});
console.log('다음 작업');
work() 가 끝난 뒤에 수행할 함수(작업)를 파라미터로 넘겨준다.
Promise
그런데 만약 비동기 작업이 많아질 때, 모두 콜백 함수로 처리하면 코드가 난잡해지게된다.
function increaseAndPrint(n, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const increased = n + 1;
console.log(increased);
if (callback) {
callback(increased);
}
}, 1000);
}
increaseAndPrint(0, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
console.log('끝!');
});
});
});
});
});
function increaseAndPrint(n, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const increased = n + 1;
console.log(increased);
if (callback) {
callback(increased);
}
}, 1000);
}
increaseAndPrint(0, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
increaseAndPrint(n, (n) => {
console.log('끝!');
});
});
});
});
});
이를 위해 만들어진 ES6에 도입된 기능이 Promise 이다.
Promise 는 성공할 수도 있고, 실패할 수도 있다. 성공할 때는 resolve 를 호출해주고, 실패할 때는 reject 를 호출한다.
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(1);
}, 1000);
});
myPromise.then((n) => {
console.log(n);
});
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(1);
}, 1000);
});
myPromise.then((n) => {
console.log(n);
});
 Younho9 Notes
Younho9 Notes