객체지향 프로그래밍(Object Oriented Programming)
객체지향 프로그래밍(Object Oriented Programming)OOPObject Oriented Programming이 글은 고현준, 송형주 님의 인사이드 자바스크립트를참조하여 작성한 글입니다.
클래스 기반 언어 vs 프로토타입 기반 언어
먼저 클래스란 같은 종류의 집단에 속하는 속성(attribute)과 행위(behavior)를 정의한 것으로, 객체지향 프로그램의 기본적인 사용자 정의 데이터형이라고 할 수 있다. 결국 클래스는 객체 생성에 사용되는 패턴 혹은 청사진일 뿐이며 new 연산자를 통한인스턴스화 과정이 필요하다.
이러한 클래스 기반 언어는 모든 인스턴스가 클래스에 정의된 대로 같은 구조이고, 보통 런타임에 그 구조를 변경할 수 없다. 이러한 특성은 정확성, 안정성, 예측성 측면에서 좋지만, 프로토타입 기반의 언어는 동적으로 자유롭게 객체의 구조와 동작 방식을 바꿀 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
자바스크립트는 클래스 개념이 없고 별도의 객체 생성 방식이 존재한다.
객체 리터럴
Object()생성자 함수생성자 함수
자바스크립트는 거의 모든 것이 객체이고, 함수 객체로 많은 것을 구현해내는데, 클래스, 생성자, 메소드도 모두 함수로 구현이 가능하다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
this.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
this.setName = function (value) {
this.name = value;
};
}
var me = new Person('zzoon');
console.log(me.getName()); // zzoon
me.setName('iamhjoo');
console.log(me.getName()); // iamhjoo
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
this.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
this.setName = function (value) {
this.name = value;
};
}
var me = new Person('zzoon');
console.log(me.getName()); // zzoon
me.setName('iamhjoo');
console.log(me.getName()); // iamhjoo
여기서 new 키워드로 새로운 객체 me 를 만든 부분을 주목하자.
var me = new Person('zzoon');
var me = new Person('zzoon');
이 형태는 기존 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어에서 한 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하는 코드와 매우 유사하다. 함수 Person 이 클래스이자 생성자의 역할을 하는 것이다.
자바스크립트에서 클래스 기반의 객체지향 프로그래밍은 기본적인 형태가 이와 같아서클래스 및 생성자의 역할을 하는 함수가 있고 사용자가 new 키워드로 인스턴스를 생성하여 사용할 수 있다.
하지만 이것은 문제가 많은 예제이다. Person 생성자 함수로 여러 객체를 만든다고해보자.
var me = new Person('me');
var you = new Person('you');
var him = new Person('him');
var me = new Person('me');
var you = new Person('you');
var him = new Person('him');
이렇게 사용하는 것은 겉으로는 별 문제 없이 작동하지만, 각 객체는 자기 영역에서공통적으로 사용할 수 있는 setName() , getName() 함수를 따로 생성하고 있어서, 중복되는 영역을 불필요하게 메모리에 올려놓고 사용하고 있다.
이러한 문제를 해결하는 방법은 자바스크립트의 프로토타입 기반의 객체지향을 이용하는 것이다.
function Person(arg) {
this.name = arg;
}
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
Person.prototype.setName = function (value) {
this.name = value;
};
var me = new Person('me');
var you = new Person('you');
console.log(me.getName());
console.log(you.getName());
function Person(arg) {
this.name = arg;
}
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
Person.prototype.setName = function (value) {
this.name = value;
};
var me = new Person('me');
var you = new Person('you');
console.log(me.getName());
console.log(you.getName());
이 예제에서는 Person 함수 객체의 prototype 프로퍼티에 getName() 과 setName() 함수를 정의했다. 이 Person 으로 객체를 생성한다면, 각 객체는 각자따로 함수 객체를 생성할 필요 없이 getName() 과 setName() 함수를 프로토타입체인으로 접근할 수 있다.
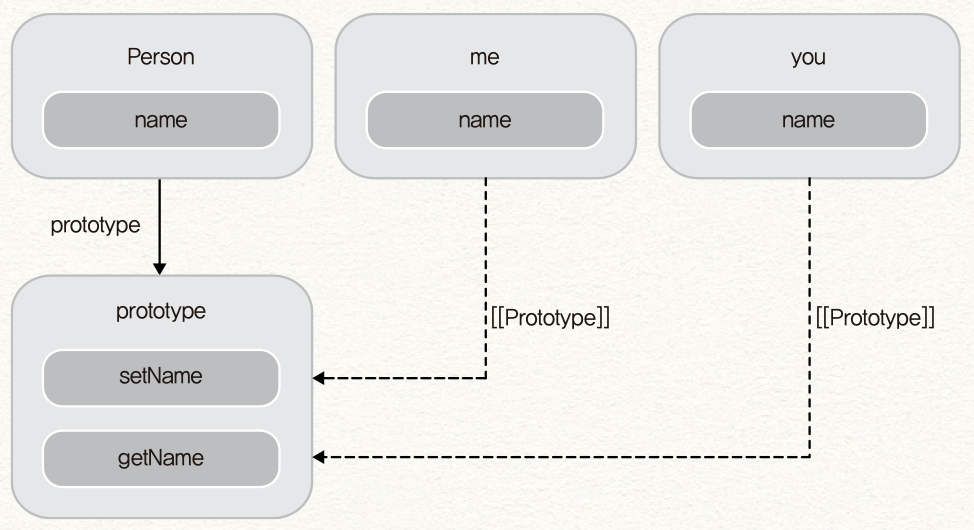
이렇게 자바스크립트에서 클래스 안의 메소드를 정의할 때는 프로토타입 객체에 정의한 후, new 로 생성한 객체에서 접근할 수 있게 하는 것이 좋다.
아래는 더글라스 크락포드가 제안한 프로토타입 객체에 메소드를 추가하는 방식이다.
Function.prototype.method = function (name, func) {
if (!this.prototype[name]) {
this.prototype[name] = func;
}
};
function Person(arg) {
this.name = arg;
}
Person.method('setName', function (value) {
this.name = value;
});
Person.method('getName', function () {
return this.name;
});
var me = new Person('me');
var you = new Person('you');
console.log(me.getName()); // me
console.log(you.getName()); // you
Function.prototype.method = function (name, func) {
if (!this.prototype[name]) {
this.prototype[name] = func;
}
};
function Person(arg) {
this.name = arg;
}
Person.method('setName', function (value) {
this.name = value;
});
Person.method('getName', function () {
return this.name;
});
var me = new Person('me');
var you = new Person('you');
console.log(me.getName()); // me
console.log(you.getName()); // you
상속
자바스크립트는 클래스를 기반으로 하는 전통적인 상속을 지원하지는 않지만, 객체 프로토타입 체인을 이용하여 상속을 구현해낼 수 있다. 이러한 상속의 구현 방식은 크게두 가지로 구분할 수 있는데, 하나는 클래스 기반 언어의 상속 방식을 흉내내는 것(의사 클래스 패턴 상속, Pseudo-classical Inheritance)이고, 두 번째는 프로토타입으로상속을 구현하는 것(프로토타입 패턴 상속, Prototypal Inheritance)이다.
의사 클래스 패턴 상속
의사 클래스 패턴은 자식 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티를 부모 생성자 함수의인스턴스로 교체하여 상속을 구현하는 방법이다.
function Person(arg) {
this.name = arg;
}
Person.prototype.setName = function (value) {
this.name = value;
};
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
function Student(arg) {}
var you = new Person('iamhjoo');
Student.prototype = you;
var me = new Student('zzoon');
me.setName('zzoon');
console.log(me.getName());
function Person(arg) {
this.name = arg;
}
Person.prototype.setName = function (value) {
this.name = value;
};
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
function Student(arg) {}
var you = new Person('iamhjoo');
Student.prototype = you;
var me = new Student('zzoon');
me.setName('zzoon');
console.log(me.getName());
이러한 방식은 몇 가지 문제를 갖고 있다.
me인스턴스를 생성할 때 부모 클래스인Person의 생성자를 호출하지 않는다.
이 코드로 me 인스턴스를 생성할 때 'zzoon' 을 넘겼으나 이를 반영하는 코드가없어서 setName() 메소드가 호출되고 나서야 me 객체에 name 프로퍼티가 만들어진다.
이를 해결하기 위해 Student 함수에 다음 코드를 추가하여 부모 클래스의 생성자를호출해야 한다.
function Student(arg) {
Person.apply(this, arguments);
}
function Student(arg) {
Person.apply(this, arguments);
}
Student 함수 안에서 새롭게 생성된 객체를 apply 함수의 첫 번째 인자로 넘겨 Person 함수를 실행시킨다.
new연산자를 통해 인스턴스를 생성한다.
생성자 함수 사용에는 위험이 존재하는데 만약 생성자 함수를 호출할 때 new 연산자를 포함하는 것을 잊게 되면, this 가 새로운 객체와 바인딩되지 않고 전역 객체에바인딩된다.
- 생성자 링크의 파괴
위 예제에서 Student 객체의 프로토타입은 Person 생성자 함수가 생성한 you 객체이다. 프로토타입 객체는 내부 프로퍼티로 constructor 를 가지며, 이는 생성자함수를 가리키는 반면 you 객체는 constructor 프로퍼티를 가지고 있지 않고, 따라서 프로토타입 체인에 의해 Person.prototype 의 constructor 인 Person 함수를가리키게 된다.
- 객체리터럴
의사 클래스 패턴 상속은 기본적으로 생성자 함수를 이용하기 때문에 객체리터럴 패턴으로 생성한 객체의 상속에는 적합하지 않다. 이는 객체리터럴 패턴으로 생성한 객체의 생성자 함수는 Object() 이고 이를 변경할 방법이 없기 때문이다.
프로토타입을 이용한 상속
프로토타입 패턴 상속은 Object.create 함수를 사용하여 객체에서 다른 객체로 직접상속을 구현하는 방식이다. 프로토타입 패턴 상속은 개념적으로 의사 클래스 패턴 상속보다 간단하며, 의사 클래스 패턴의 단점인 new 연산자가 필요없고 생성자 링크도파괴되지 않으며 객체 리터럴에도 사용할 수 있다.
 Younho9 Notes
Younho9 Notes